Cluster Drive Creation
Use this procedure to create a new Cluster Drive (Ceph-backed storage) in eEKAS. The example below walks through creating an Erasure Coding drive.
Before you start creating ceph cluster drive
- Decide the protection method (Replication or Erasure Coding).
- Know the purpose (general Storage for SMB/NFS/iSCSI/NVMe‑oF, or S3).
- Make sure you have the same number of free disks on every node—eEKAS requires a balanced selection.
1) Click Create Cluster Drive
Open Cluster Drives in the UI and select Create Cluster Drive to launch the wizard.
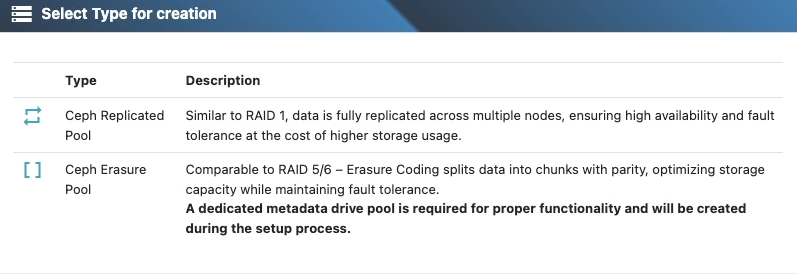
2) Choose the protection method
Select Replication or Erasure Coding.
For this example, choose Erasure Coding.
Tip: If you’re unsure, see Replication vs. Erasure Coding for pros/cons and examples.
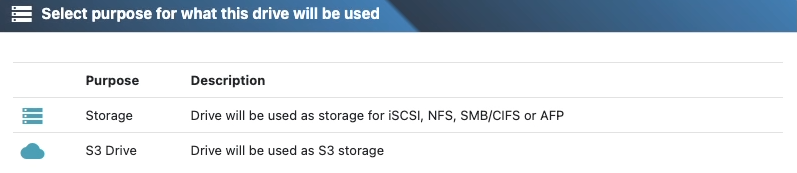
3) Select the purpose
Pick storage (SMB, NFS, iSCSI, NVMe‑oF) or S3
Note: S3 Cluster Drives will automatically create all nessesary pools
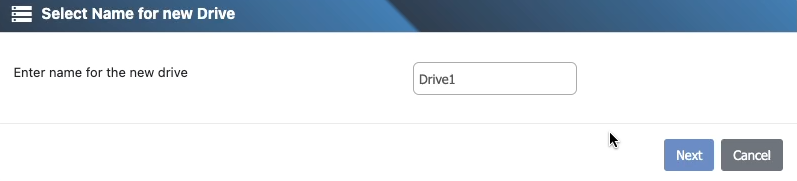
4) Name the drive
Enter a unique, descriptive Name for the Cluster Drive.
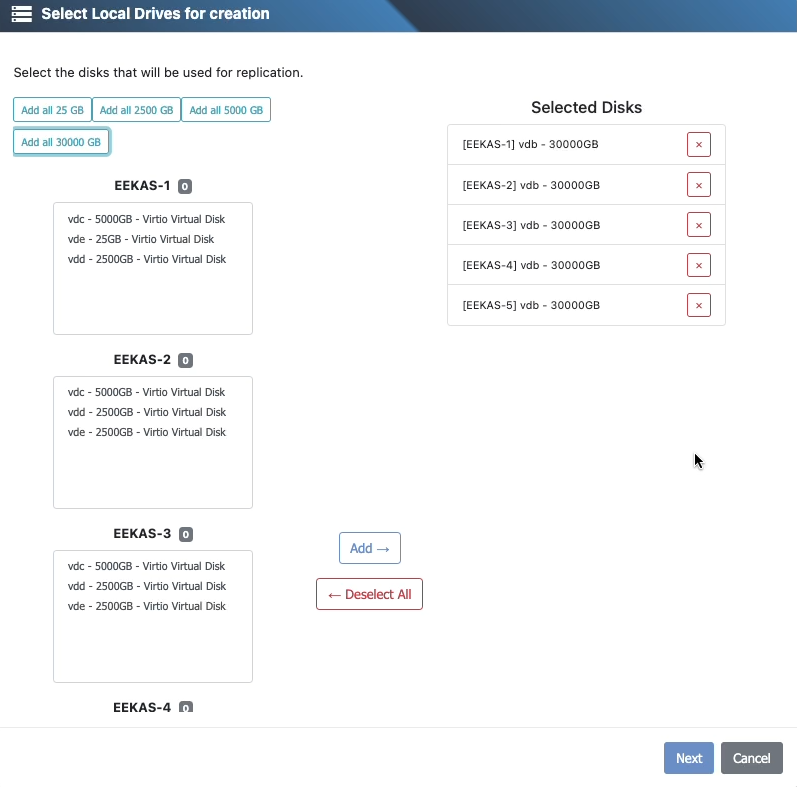
5) Select data disks on each node
Choose disks per node, ensuring you select the same count on every node.
You can add disks by:
Selecting them and clicking Add, or
Double‑clicking each disk.
Important: The wizard enforces symmetry. If counts differ between nodes, you’ll be prompted to adjust.
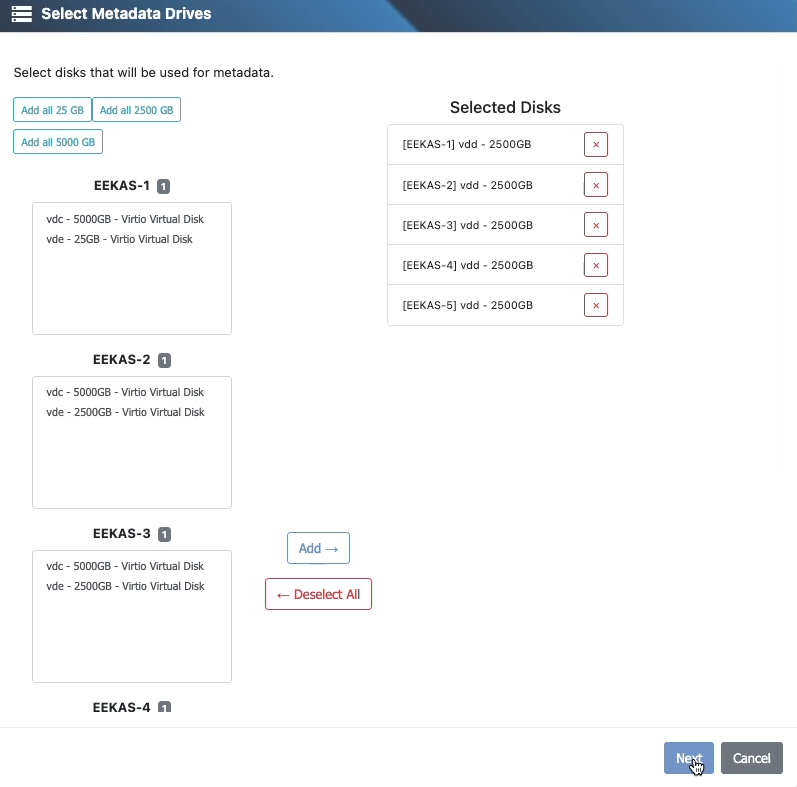
6) Select metadata disks
Replication: Selecting metadata disks is optional but recommended.
Erasure Coding: Selecting metadata disks is required. The wizard will move to the Metadata Disks page.
Tip: For best responsiveness, place metadata on fast, reliable media such as SSD or NVMe
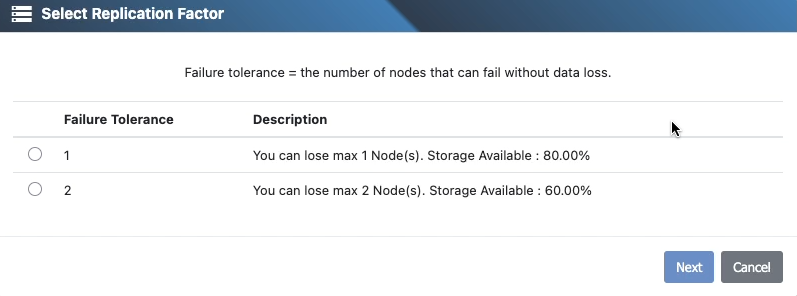
7) Choose fault tolerance
Set the redundancy level for the drive (see the Replication vs. Erasure Coding article for details and guidance).
Each option will also provide you information about estimated usable capacity
Examples
Replication: 3× replication (three full copies)
Erasure Coding: 5+2 (five data chunks + two parity chunks)
Capacity basics:
Replication usable ≈ raw / copies (e.g., 3× → ~33%).
Erasure coding usable ≈ k / (k+m) (e.g., 5+2 → ~71%).
Minimum disk counts must meet or exceed the selected profile.
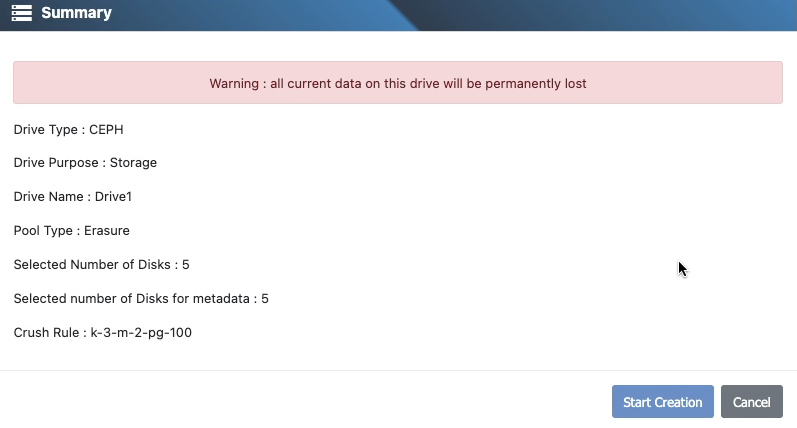
8) Review the summary
A summary page shows:
- Protection method and fault-tolerance profile
- Purpose and resulting pool layout (single‑ or multi‑pool)
- Selected data and metadata disks (per node)
- Estimated usable capacity
If everything looks correct, click Create to provision the Cluster Drive.
Troubleshooting & Tips
Unbalanced selection: Ensure each node has the same number of selected disks.
Performance tuning: Use replication for low‑latency, high‑IOPS workloads; use erasure coding for large, capacity‑oriented datasets (e.g., S3, archives).