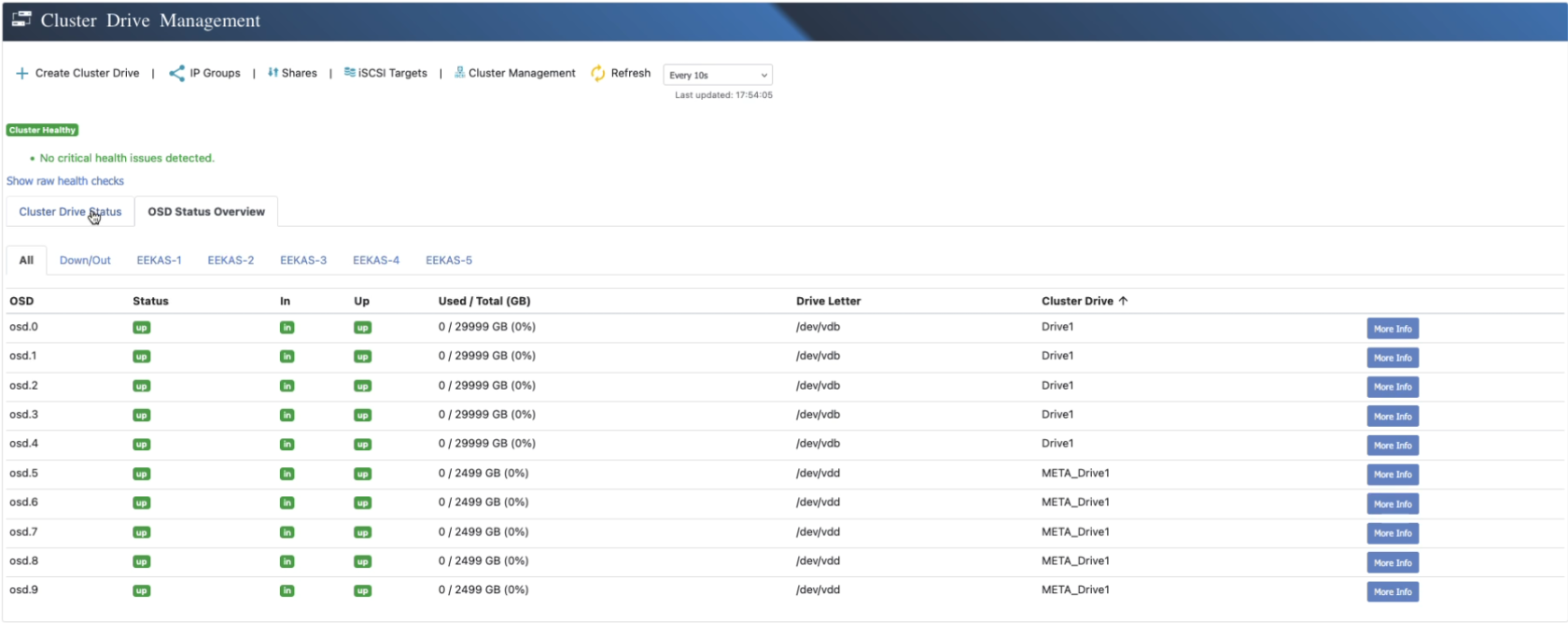
Understanding OSDs in Ceph
In a Ceph cluster, an OSD (Object Storage Daemon) is the process responsible for storing data on a
physical disk. Each OSD manages a single storage device and handles tasks such as data replication, erasure coding,
recovery, rebalancing, and reporting disk status back to the cluster monitor.
The number of OSDs in a cluster directly impacts capacity, performance, and fault tolerance. Since Ceph distributes
objects across all available OSDs, losing one or more OSDs does not automatically result in data loss—this depends on
the protection policy chosen (Replication or Erasure Coding).
Fault Tolerance and OSD Loss
Replication
With replication, Ceph stores identical copies of data on multiple OSDs across different nodes. The
replication factor determines how many OSDs can fail without data loss:
- 2× Replication – Two copies of each object. The cluster can lose one OSDwithout data
loss. - 3× Replication – Three copies of each object. The cluster can lose two OSDswithout
data loss. - N× Replication – In general, with N copies, the cluster can lose (N-1) OSDs
that hold the same object.
Erasure Coding
With erasure coding, data is divided into K data chunks plus M parity chunks. These
chunks are distributed across different OSDs. The cluster can tolerate up to M OSD failures without
losing data.
- 4+2 EC – Data is split into 4 data chunks + 2 parity chunks. Can tolerate the loss of
2 OSDs. - 5+2 EC – Data is split into 5 data chunks + 2 parity chunks. Can tolerate the loss of
2 OSDs. - 8+3 EC – Data is split into 8 data chunks + 3 parity chunks. Can tolerate the loss of
3 OSDs.
Key Considerations
- OSDs should be distributed across multiple nodes to ensure high availability. Losing multiple OSDs on the same
node may impact services if redundancy requirements are not met. - Replication offers faster recovery and lower CPU overhead but requires more storage capacity.
- Erasure Coding provides higher storage efficiency but requires more CPU/network resources for encoding and recovery.
In summary, the number of OSDs you can safely lose depends on whether your Cluster Drive uses Replication
or Erasure Coding—and on the redundancy level you selected when creating it.